Hello people, it’s been a while since I have posted projects on this website. This semester was really busy, I didn’t have time to much else, but soon I will have my winter holiday (Here in south our summer holiday is from December to February).
Today I am going to show you how to build a simple temperature sensor using one LM35 Precision Temperature Sensor and Arduino, so you can hookup on your future projects. The circuit will send serial information about the temperature so you can use on your computer, change the code as you will. I’m planning to build a temperature sensor with max/min + clock + LCD, and when I get it done, I will post here.
Parts:
- Arduino (You can use other microcontroller, but then you will need to change the code).
- LM35 Precision Centigrade Temperature Sensor, you can get from any electronic store. Here is the DATA SHEET.
- BreadBoard
This is a quick and simple step. Just connect the 5V output from arduino to the 1st pin of the sensor, ground the 3rd pin and the 2nd one, you connect to the 0 Analog Input.
Down goes some pictures that may help you, click to enlarge:


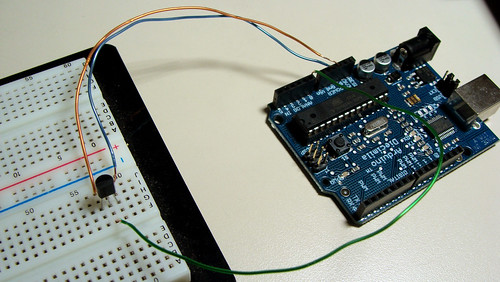
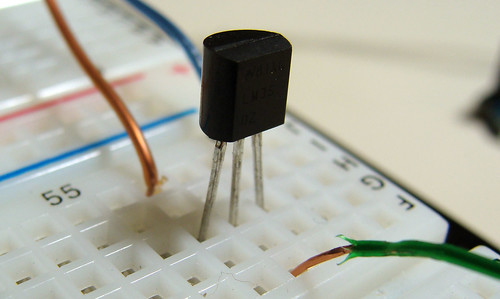
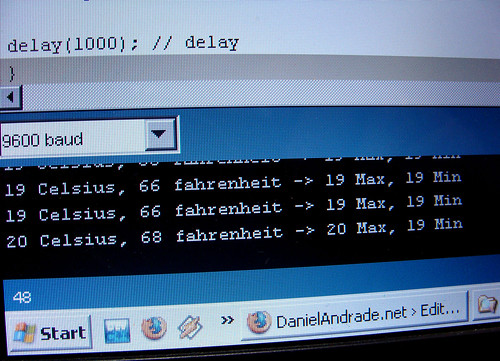
Here is the Arduino Code, just upload it and check the Serial Communication Option.
You can also download the .pde HERE.
/*
An open-source LM35DZ Temperature Sensor for Arduino. This project will be enhanced on a regular basis
(cc) by Daniel Spillere Andrade , http://www.danielandrade.net
http://creativecommons.org/license/cc-gpl
*/
int pin = 0; // analog pin
int tempc = 0,tempf=0; // temperature variables
int samples[8]; // variables to make a better precision
int maxi = -100,mini = 100; // to start max/min temperature
int i;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial communication
}
void loop()
{
for(i = 0;i< =7;i++){ // gets 8 samples of temperature
samples[i] = ( 5.0 * analogRead(pin) * 100.0) / 1024.0;
tempc = tempc + samples[i];
delay(1000);
}
tempc = tempc/8.0; // better precision
tempf = (tempc * 9)/ 5 + 32; // converts to fahrenheit
if(tempc > maxi) {maxi = tempc;} // set max temperature
if(tempc < mini) {mini = tempc;} // set min temperature
Serial.print(tempc,DEC);
Serial.print(" Celsius, ");
Serial.print(tempf,DEC);
Serial.print(" fahrenheit -> ");
Serial.print(maxi,DEC);
Serial.print(" Max, ");
Serial.print(mini,DEC);
Serial.println(" Min");
tempc = 0;
delay(1000); // delay before loop
}
An open-source LM35DZ Temperature Sensor for Arduino. This project will be enhanced on a regular basis
(cc) by Daniel Spillere Andrade , http://www.danielandrade.net
http://creativecommons.org/license/cc-gpl
*/
int pin = 0; // analog pin
int tempc = 0,tempf=0; // temperature variables
int samples[8]; // variables to make a better precision
int maxi = -100,mini = 100; // to start max/min temperature
int i;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial communication
}
void loop()
{
for(i = 0;i< =7;i++){ // gets 8 samples of temperature
samples[i] = ( 5.0 * analogRead(pin) * 100.0) / 1024.0;
tempc = tempc + samples[i];
delay(1000);
}
tempc = tempc/8.0; // better precision
tempf = (tempc * 9)/ 5 + 32; // converts to fahrenheit
if(tempc > maxi) {maxi = tempc;} // set max temperature
if(tempc < mini) {mini = tempc;} // set min temperature
Serial.print(tempc,DEC);
Serial.print(" Celsius, ");
Serial.print(tempf,DEC);
Serial.print(" fahrenheit -> ");
Serial.print(maxi,DEC);
Serial.print(" Max, ");
Serial.print(mini,DEC);
Serial.println(" Min");
tempc = 0;
delay(1000); // delay before loop
}
Anything just ask!
Source by : link
Comments
Post a Comment