In many projects use is made of alphanumeric LCDs that are driven internally by Hitachi’s industry-standard HD44780 controller. These displays can be driven either in 4-bit or 8-bit mode. In the first case only the high nibble (D4 to D7) of the display’s data bus is used. The four unused connections still deserve some closer attention. The data lines can be used as either inputs or outputs for the display. It is well known that an unloaded output is fine, but that a floating high-impedance input can cause problems. So what should you do with the four unused data lines when the display is used in 4-bit mode? This question arose when a circuit was submitted to us where D0-D3 where tied directly to GND (the same applies if it was to +5 V) to stop the problem of floating inputs.
The LCD module was driven directly by a microcontroller, which was on a development board for testing various programs and I/O functions. There was a switch present for turning off the enable of the display when it wasn’t being used, but this could be forgotten during some experiments. When the R/Wline of the display is permanently tied to GND (data only goes from the microcontroller to the display) then the remaining lines can safely be connected to the supply (+ve or GND). In this application however, the R/Wline was also controlled by the microcontroller. When the display is initialised correctly then nothing much should go wrong. The data sheet for the HD44780 is not very clear as to what happens with the low nibble during initialisation.
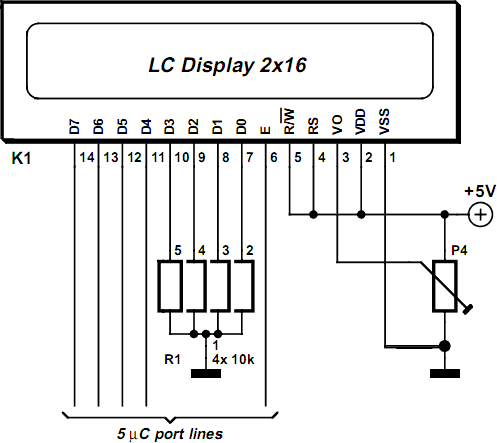
LCD Module in 4-bit Mode Circuit Diagram
After the power-on reset the display will always be in 8-bit mode. A simple experiment (see the accompanying circuit) reveals that it is safer to use pull-down resistors to GND for the four low data lines. The data lines of the display are configured as outputs in this circuit (R/Wis high) and the ‘enable’ is toggled (which can still happen, even though it is not the intention to communicate with the display). Note that in practice the RS line will also be driven by an I/O pin, and in our circuit the R/W line as well. All data lines become high and it’s not certain if (and if so, for how long) the display can survive with four shorted data lines. The moral of the story is: in 4-bit mode you should always tie D0-D3 via resistors to ground or positive.
Author: L. Lemmens
Copyright: Elektor Electronics
Copyright: Elektor Electronics
Comments
Post a Comment