This is a simple project of Line Following Robot Sensor Circuit Diagram. This Line Following Robot sensor or surface scanner for robots is a very simple, stamp-sized, short range (5-10mm) Infrared proximity detector wired around a standard reflective opto-sensor CNY70(IC1). In some disciplines, a line following robot or an electronic toy vehicle go along a predrawn black line on a white surface. In such devices, a surface scanner, pointed at the surface is used to align the right track.
IC1 contains an infrared LED and a phototransistor. The LED emit invisible infrared light on the track and the phototransistor works as a receiver. Usually, black colored surface reflects less light than white surface and more current will flow through the phototransistor when it is above a white surface. When a reflection is detected (IR light falls on the phototransistor) a current flows through R2 to ground which generates a voltage drop at the base of T1 to make it conduct. As a result, transistor T2 start conducting and the visual indicator LED(D1) lights up. Capacitor C2 works as a mini buffer.
Line Follower Robot Scanner Schematic
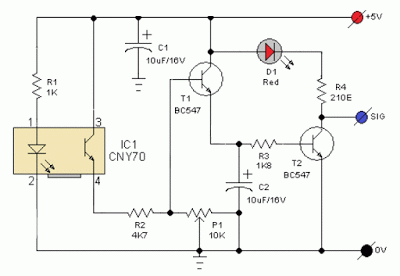
IC1 contains an infrared LED and a phototransistor. The LED emit invisible infrared light on the track and the phototransistor works as a receiver. Usually, black colored surface reflects less light than white surface and more current will flow through the phototransistor when it is above a white surface. When a reflection is detected (IR light falls on the phototransistor) a current flows through R2 to ground which generates a voltage drop at the base of T1 to make it conduct. As a result, transistor T2 start conducting and the visual indicator LED(D1) lights up. Capacitor C2 works as a mini buffer.
Line Follower Robot Scanner Schematic

After construction and installation, the scanner needs to be calibrated. Initially set P1 to its mechanical centre position and place the robot above the white portion of the track. Now slowly turn P1 to get a good response from D1. After this, fine tune P1 to reduce false detection caused by external light sources. Also ensure that the LED remains in off condition when the sensor module is on the blackarea. Repeat the process until the correct calibration is achieved.
The red color LED (D1) is only a visual indicator. You can add a suitable (5V) reed relay in parallel with D1-R4 wiring after suitable alterations to brake/stop/redirect the robot. Similarly, the High to low (H-L) transition at the collector of T2 can be used as a signal to control the logic blocks of the robot. Resistor R1 determines the operating current of the IRLED inside IC1. The sensing ability largely depends on the reflective properties of the markings on the track and the strength of the light output from IC1.
The red color LED (D1) is only a visual indicator. You can add a suitable (5V) reed relay in parallel with D1-R4 wiring after suitable alterations to brake/stop/redirect the robot. Similarly, the High to low (H-L) transition at the collector of T2 can be used as a signal to control the logic blocks of the robot. Resistor R1 determines the operating current of the IRLED inside IC1. The sensing ability largely depends on the reflective properties of the markings on the track and the strength of the light output from IC1.
Comments
Post a Comment